 |
| To view a brief explanation of a process, click the icon
for the process you want to hear about. |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
Materials acceptance
Acceptance checking is carried out on the
materials used to manufacture products, and only materials that have
passed the checks are so identified and then stored in the appropriate
area according to grade and intended use. |
 |
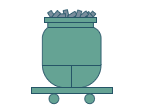
Charging
The correct steel scraps are chosen from
the 16 areas where scrap is stored according to the grade intended
use, and put in buckets ready to be loaded into the electric arc furnace. |
 |
Weighing and blending steel scraps
We use a unique calculation method that divides
80 tons of scrap steel into three lots, to be weighed and blended. |
 |
£Back
to Manufacturing Process Diagram |
|
 |
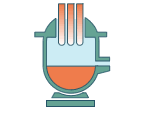 |
Melting and refining
The loaded scrap steel is melted in the electric
arc furnace, and refined to remove impurities. Pure steel is the result. |
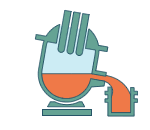 |
Tapping out
Once the refined molten steel is confirmed
to have reached the prescribed temperature, it is transferred to the
ladle. |
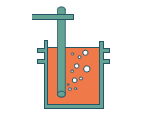 |
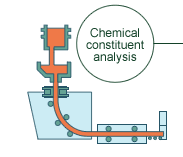
Bubbling
Nitrogen gas is used inside the ladle to
blend the contents. This process evens out the chemical constituent
and temperature of the molten steel. |
 |
£Back
to Manufacturing Process Diagram |
|
|
 |
 |
Continuous casting
Continuous casting is used to cast billets
(semi-finished rectangular rods) in a mold from molten steel. |
|
| £Back
to Manufacturing Process Diagram |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The turner
The turner changes the direction of the
billets as they come from the continuous casting process, to prepare
them for rolling. |
The billet yard
The billet yard is where billets (semi-finished
products) that were produced during the continuous casting process
are stored. |
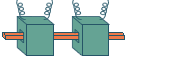
Induction heating
When direct rolling is to be done, the
temperature of the billets is finely adjusted, as necessary, in
preparation for the rolling process. |
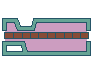
Heating
To prepare for cold rolling, the billets
are heated to the correct temperature for the rolling process. |
|
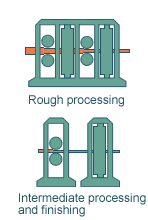 |
Rolling
The billets are forged alternately vertically
and horizontally on the HV stand, until they meet the rolling size
required to make the desired finished product. |
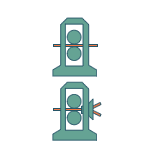 |
Slit (D10-D16)
One billet is divided lengthwise into equal
left and right pieces, leading to the creation of two finished products.
 |
 |
Cooling
The rolled products are left standing to
cool. |
 |
£Back
to Manufacturing Process Diagram |
|
 |
 |
Shearing
The rolled products are cut to the specified
length, which can be from 3.5 m to 12 m long. |
 |
 |
Binding and weighing
The products cut to specified length are
bound with the appropriate number in each bundle, and the weight of
each bundle is then checked. |
 |
 |
Shipping
The products are delivered to the customer'
designated location. |
 |
£Back
to Manufacturing Process Diagram |
|
